List of commonly used bamboo types: Bambusa, Chusquea, Dendrocalamus, Gigantochloa, Guadua, Phyllostachys
Positive Environmental Effects
Biomass Production: Bamboo is a rapid-growth natural resource that can produce much more dry biomass per hectare per year than eucalyptus. Reduction of Soil Erosion: Bamboo has a dense network of roots that anchors earth and helps to lessen erosion due to rain and flooding. Water Retention: One hectare of Guadua angustifolia can retain over 30,000 liters of water. Regulation of Hydraulic Flow: Retaining water in its stem, bamboo conserves water in the rainy season, using it later in the dry season. Temperature Reduction: Thanks to their leaves, bamboo forests reduce air temperature through water evaporation. Sequestering of CO2: Plants that assimilate CO2 for photosynthesis, storing it in their biomass, make an important contribution to the global climate. Primary Energy: the production of bamboo uses 300 MJ/m3, compared with 600 MJ/m3 for wood.
Different Uses:
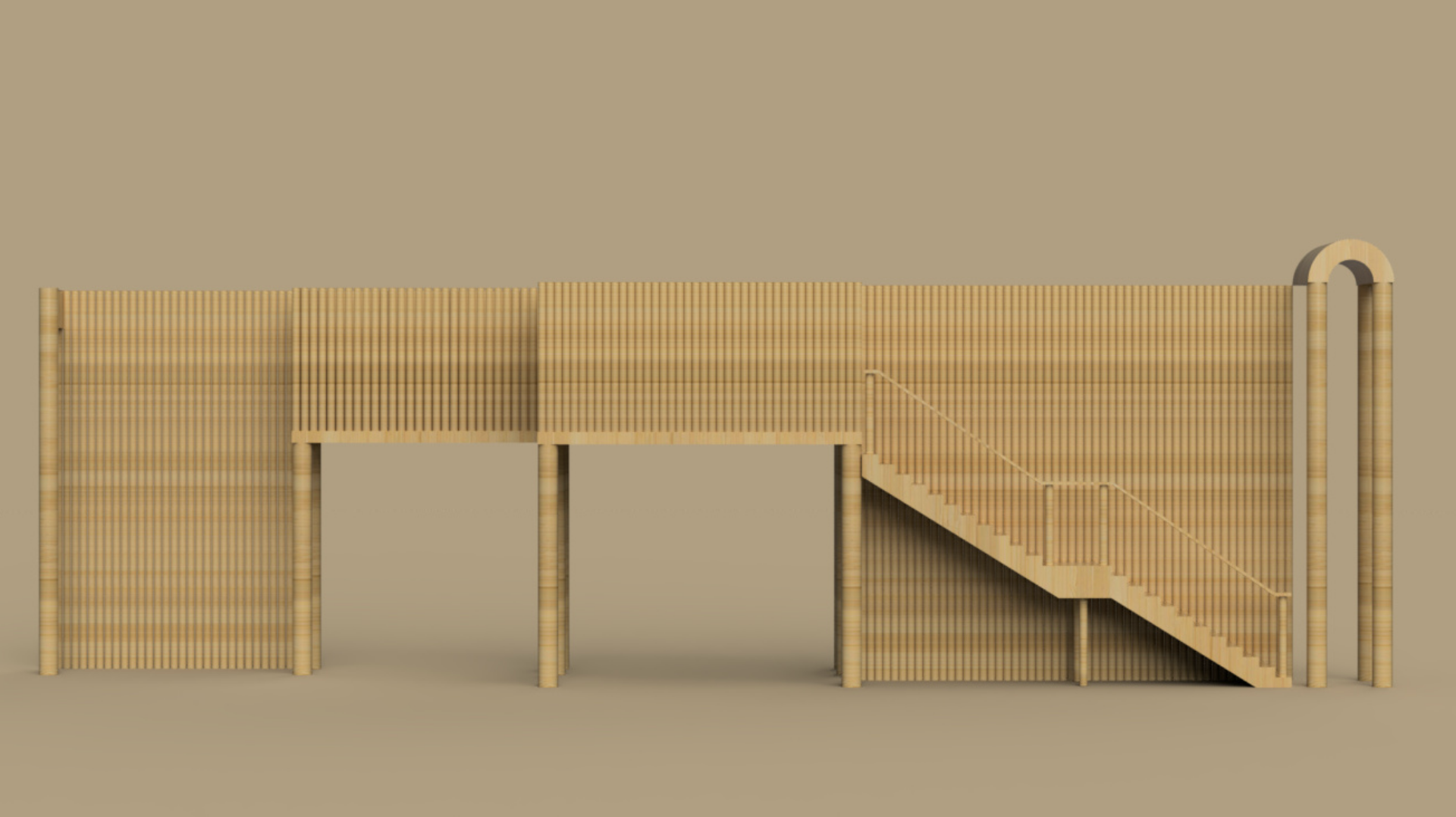
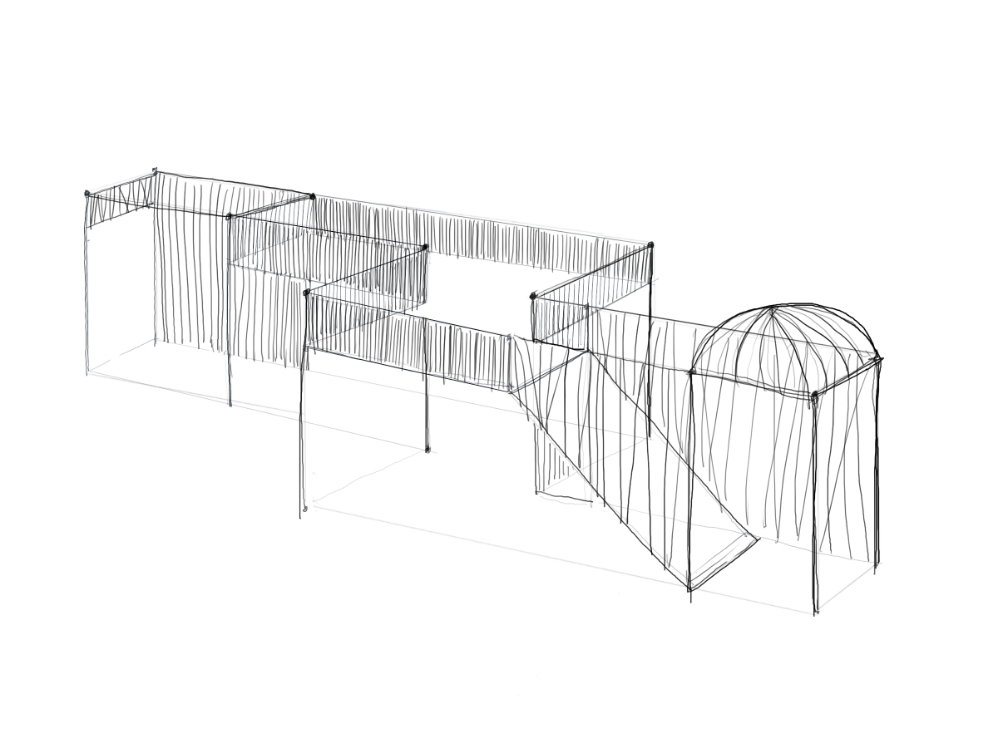
The use depends on the type of bamboo, its age and the part of the plant. Due to its favourable mechanical characteristics, great flexibility, rapid growth, low weight and low cost, bamboo is a construction material with many applications. It is estimated that one billion people live in houses constructed from bamboo. Another common use in regions where bamboo grows is for crafts and everyday objects, musical instruments and furniture. New is the experimental use in vehicles like bicycles, cars and buses.
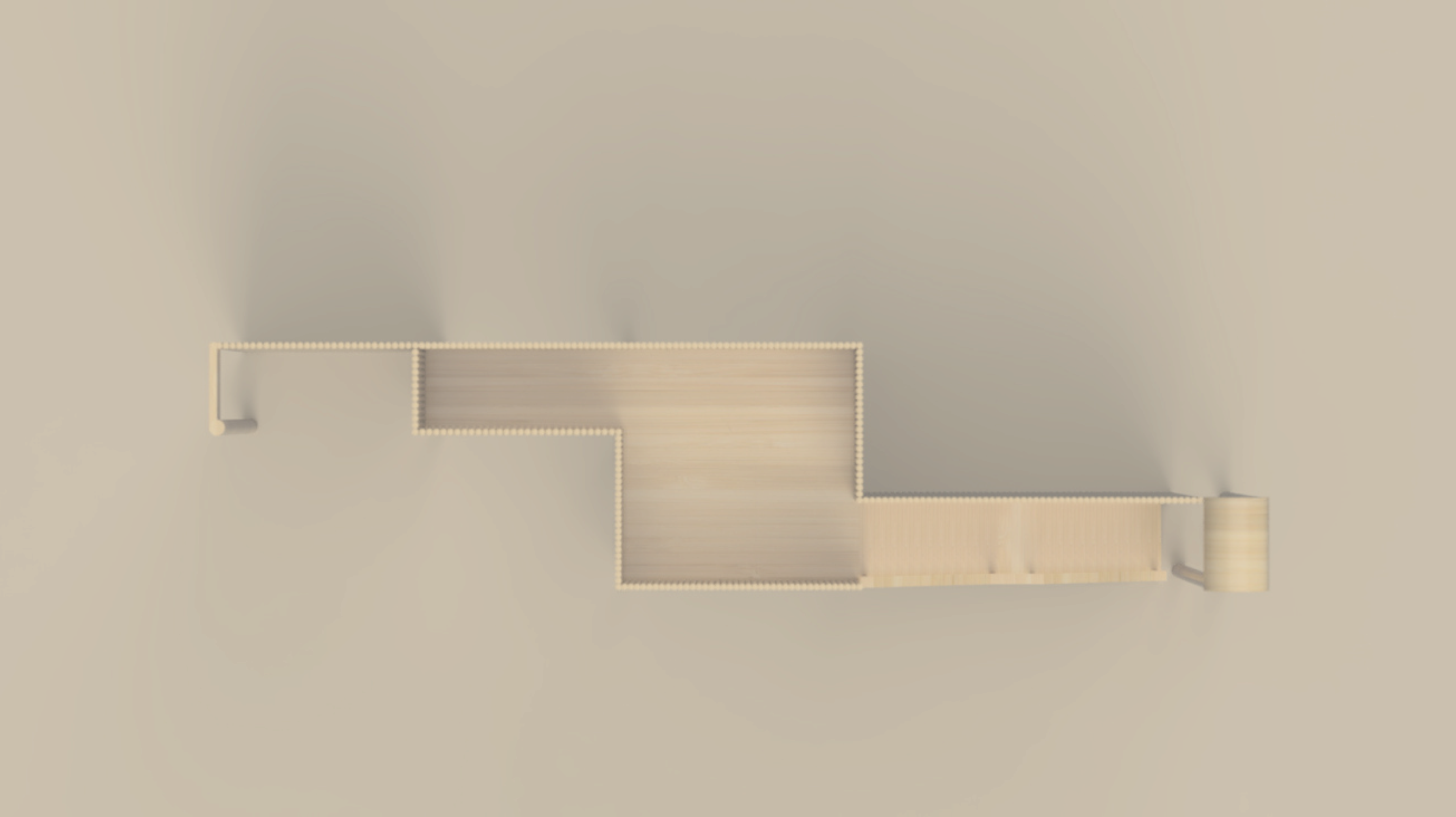
General Aspects of Constructruction:
Advantages: Light, forms structure that have a low mass-to-flexibility ratio compared with those of wood. The external layer of the shell offers very high resistance to tension, equalling that of steel. Bamboo grows extremely rapidly and is usable as a construction material after four to six years. Laminated bamboo, as used for example for floors, shows and extreme resistance to abrasion.
Disadvantages: Its structural behavior can vary depending on the species, the growing site, its age, the moisture content and the part of the stalk that is used. Bamboo is vulnerable to exposure to ultraviolet rays and rain. It is also sensitive to attack from insects and fungus. Its round section and its tendency to crack easily complicates the execution of joints and supports.